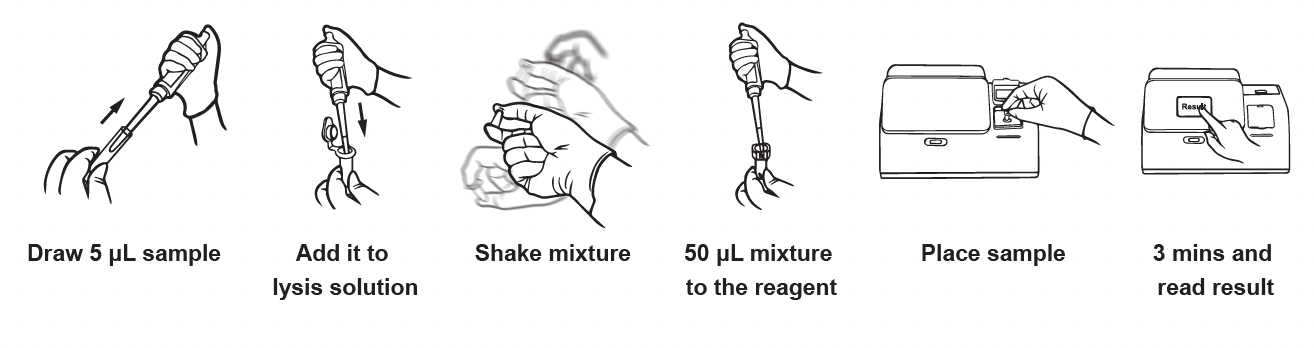
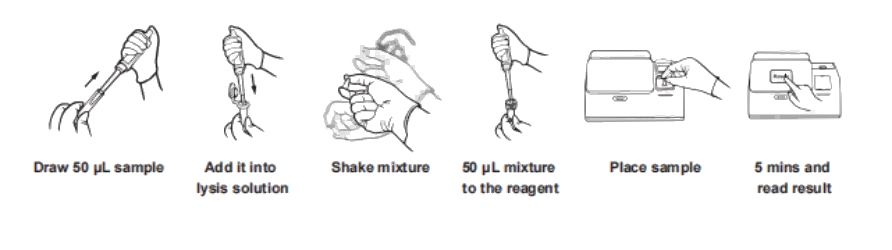
Biological sample collection is a cornerstone of clinical research, providing critical data for evaluating drug pharmacokinetics (PK), immunogenicity, efficacy, and safety. Diverse specimen containers are employed for various sample types, ranging from common biological fluids like blood (whole blood, serum, plasma), urine, and feces, to more specialized in vivo samples such as arterial blood, saliva, cerebrospinal fluid, alveolar lavage fluid, wound exudate, tears, pathological tissue, and skin microdialysis samples. In studies involving viral vector test drugs, samples may also include those from the nose and wound surfaces, or even dressings.
The overarching purpose of sample collection dictates the specific design, categorized into PK, immunogenicity, efficacy/exploratory pharmacodynamic (PD), and safety sample collection. This document primarily details the design methodology for PK sample collection, with brief insights into considerations for efficacy/PD, safety, and immunogenicity evaluations.
Design of Pharmacokinetic (PK) Sample Collection
The fundamental principle guiding PK sampling point design is to balance thorough coverage of pharmacokinetic characteristics with minimizing burden on subjects and researchers. Sampling points should be as concise and infrequent as possible while ensuring subject safety and encompassing the entire PK profile. Ideally, sampling points should align with study visit points, and sampling times should be scheduled to avoid disrupting sleep, though exceptions may arise.
Beyond time points, the entire sampling process—including collection, processing, and storage environment—is critical. The selection of anticoagulants, temperature, and processing time limits must be explicitly defined. If not detailed in the study protocol, these specifics require precise documentation in an independent sample processing manual.
PK studies necessitate evaluating not only the parent drug's metabolic characteristics but also those of its primary active metabolites. A judicious selection of sampling times is crucial, typically informed by non-clinical research, predicted or existing human PK data, and formulation characteristics. The sampling points must span the absorption, distribution, and elimination phases to comprehensively describe the drug's PK in the human body.
Potential interferences from diet, time of day, and other factors must be considered.
- First-in-Human (FIH) trials commonly involve single and multiple dose PK evaluations.
- Subsequent PK studies, such as food effect or drug-drug interaction (DDI) studies, can be conducted as needed.
- FIH trials are generally conducted in healthy subjects or patient populations.
- If the test drug exhibits a less favorable safety profile, patient populations are typically prioritized.
-
For studies with limited subject numbers (e.g., rare diseases), or where intensive blood collection is impractical due to patient conditions (e.g., cancer, blood disorders, critically ill patients) or special populations like children, a multi-dose sparse sampling population pharmacokinetic (PPK) study might be considered for PK investigation.
Detection Indicators:
Single-Dose Administration: Tmax (time to maximum concentration), Cmax (maximum concentration), AUC (0-t) (area under the curve from time 0 to t), AUC (0-∞) (area under the curve from time 0 to infinity), Vd (volume of distribution), Kel (elimination rate constant), t1/2 (half-life), MRT (mean residence time), CL (clearance) or CL/F (apparent clearance).
Multiple-Dose Administration: Peak time (Tmax), steady-state trough concentration (Css_min), steady-state peak concentration (Css_max), average steady-state blood drug concentration (Css_av), elimination half-life (t1/2), clearance (CL or CL/F), area under the steady-state blood drug concentration-time curve (AUCss), and fluctuation coefficient (DF).
Sampling Points Specifics:
- At least 2-3 sampling points are required pre-medication.
- The absorption phase should include at least 3 sampling points at or around peak concentration.
- The distribution and elimination phases should include at least 3-5 sampling points.
Generally, a minimum of 11-12 sampling points are recommended, extending for 3-5 elimination half-lives, or until the drug concentration falls to 1/20 to 1/10 of Cmax.
Commonly, 12-20 sampling points are utilized. For long half-life test drugs, sampling typically extends for at least 72 hours.
For multiple administrations, trough concentrations (prior to administration) should be measured three times (usually for three consecutive days) to confirm the achievement of steady-state conditions. A series of blood samples are then collected after the final administration.
Sampling points are ideally arranged for fasting administration in the morning to mitigate interference from diet, time of day, and other confounding factors.
Route of Administration Considerations:
Different routes of administration (e.g., intravenous injection, intravenous drip, nebulized inhalation) exhibit distinct PK characteristics, necessitating route-specific sampling point designs. For instance, intravenous injection lacks an absorption phase. Intravenous drip and nebulized inhalation, however, typically require sample collection pre-administration, immediately before administration, and 5-10 minutes post-administration or at the end of administration.
For urine/feces collection, samples should be taken at various intervals pre- and post-medication. The determination of these sampling points can be informed by drug excretion characteristics observed in animal PK studies, encompassing the onset of excretion, peak excretion, and the approximate end of the excretion process.
General PK Collection Process:
Subjects typically enter the Phase I clinical trial ward the day before the study, consuming a standardized light dinner followed by a 10-hour fast (not necessarily overnight).
The next morning, the drug is administered orally on an empty stomach (fasting is not required for injections), accompanied by 200-250ml of water. If urine samples are required, the bladder should be emptied before drug administration. Blood or urine samples are then collected at specific time points before and after dosing, as per the study plan.
For urine samples, the total volume should be recorded, and the required aliquot retained. Subjects generally remain within the Phase I clinical trial ward for the duration of the trial, avoiding strenuous exercise, consumption of caffeinated or alcoholic beverages, and smoking.
Other Sample Collection Precautions
Immunogenicity and Efficacy/Exploratory PD Sample Collection:
Specimen container collection for immunogenicity and efficacy/exploratory PD requires careful consideration of relevant signaling pathway response characteristics and alignment with other planned biological sample collection time points.
Immunogenicity responses to biological products are typically not immediate. The initial post-treatment immunogenicity specimen container collection can be set at 21-28 days after administration (EMA recommends no earlier than 4 weeks post-last dose), but never earlier than 14 days. The impact of existing subject reactivity to therapeutic biological products on the immunogenicity response time should also be considered. The frequency of sampling points and the extent of analysis depend on the test drug's risk assessment.
For efficacy/PD-related samples, such as glycated hemoglobin in diabetes studies, sampling points are determined by integrating the pharmacological time-effect relationship (onset, duration, optimal efficacy), prior monitoring experience, and preclinical animal study data. To ensure reproducibility of efficacy data, protocols may specify that samples are collected within a relatively fixed time period.
Safety Sample Collection:
Laboratory examination time points for safety assessments are typically designed in conjunction with pharmacokinetic characteristics. The general principle is to have denser sampling points initially, becoming sparser later (applicable after a single dose, during long-term administration, and in early clinical research for clinical practice verification).
It's generally understood that after five consecutive doses, blood drug concentrations can reach a steady state. For drugs with ideal metabolism that achieve steady-state blood concentrations, if steady-state levels are confirmed safe for subjects, the interval between subsequent sampling points can be extended. However, for experimental drugs that may exhibit blood drug accumulation, close monitoring of potential safety impacts is crucial, necessitating a relatively dense schedule for safety visit points.