World Prematurity Day: Preeclampsia Tests for Early Preterm Birth Risk Assessment
1.Introduction: The Silent Threat of Preeclampsi
November 17th is observed as World Prematurity Day, a global effort to raise awareness of the challenges of preterm birth. According to World Health Organization data, approximately 15 million babies are born prematurely worldwide annually, of which nearly 1 million succumb to complications related to preterm birth. Among the key drivers of medically-indicated preterm birth is preeclampsia, a serious multi-system disorder unique to pregnancy.
Preeclampsia is characterized primarily by new-onset hypertension (≥140/90 mmHg) and proteinuria after 20 weeks of gestation. It can lead to placental insufficiency and fetal growth restriction, thereby triggering preterm birth (delivery before 37 weeks of gestation). The core mechanism of preeclampsia involves an imbalance in placental angiogenesis, with abnormal changes in sFlt-1 and PIGF serving as key early warning signals.
2.sFlt-1 and PIGF: "Biological Early Warning Indicators" for Preterm Birth Risk
● Soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase-1 (sFlt-1): As an anti-angiogenic factor, its over-secretion inhibits the activity of PIGF and VEGF, leading to placental ischemia and hypoxia, which can trigger preterm birth.
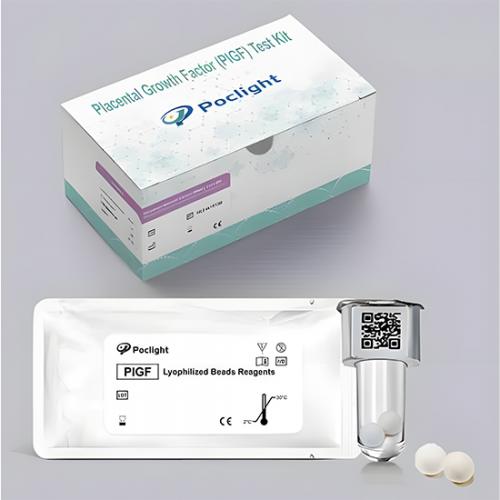
● Placental Growth Factor (PIGF):A pro-angiogenic factor; decreased levels reflect impaired placental function and are positively correlated with preterm birth risk.
● Interpreting the sFlt-1/PIGF Ratio: A Key Indicator for Risk Stratification
Ratio ≤ 38: A negative predictive value of 99.3%, can rule out the onset of PE within one week, helping to avoid unnecessary interventions.
Ratio > 38: Indicates a significantly increased risk of PE within four weeks, warranting intensified monitoring.
Ratio > 10: The risk of early-onset PE increases fivefold, necessitating vigilance for adverse outcomes such as fetal growth restriction.
3.Clinical Significance :Dynamic Monitoring
Patients with an elevated ratio in the mid-to-late trimester require shorter intervals between prenatal check-ups and intensified blood pressure and fetal monitoring.
● First Trimester (11-13+6 weeks): PIGF combined with maternal factors (such as age, BMI) predicts PE risk, guiding early intervention.
● Mid-to-Late Trimester (14-34+6 weeks): Dynamic monitoring of the sFlt-1/PIGF ratio enables short-term prediction of early-onset PE and assessment of disease severity.
● Patients Diagnosed with PE: Changes in the ratio can predict adverse pregnancy outcomes and guide the timing of delivery.
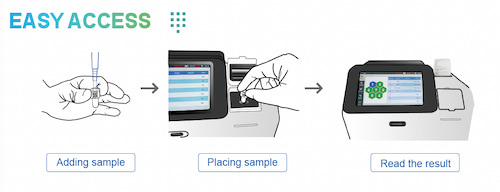
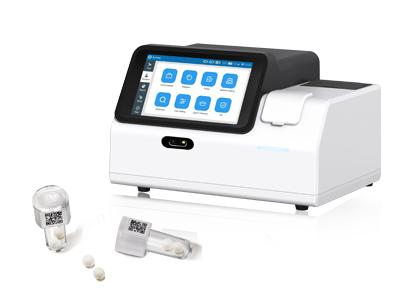
The realization of this test's value relies on the support of chemiluminescence(CL) resonanceenergy transfer(CRET) technology and chemiluminescence immunoassay analyzers. The Placental Growth Factor ( PIGF) and Soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase-1 (sFlt-1) Test Kit (Homogeneous Chemiluminescent Immunoassay) is a two-site ("sandwich") chemiluminescent immunoassay based on Chemiluminescence (CL) Resonance Energy Transfer (CRET) technology. It can accurately capture minute changes in these biomarkers in the blood through highly specific antigen-antibody reactions, providing reliable data for clinical decision-making. To facilitate clinical interpretation, the sFlt-1/PlGF ratio is automatically computed from a single sample.
Key Advantage (vs. Traditional ELISA):
● Exceptional Speed: Reduces the detection time from 3 hours to just 5 minutes.
● Operational Simplicity:The homogeneous assay format removes the need for cumbersome washing and separstion steps.